Medical abbreviations are essential for healthcare professionals, providing a shorthand method for documenting patient information quickly and accurately. However, some abbreviations can be confusing if not properly understood or used. One such abbreviation that is crucial in various healthcare settings is “TDWB.” In this post, we will explore the TDWB medical abbreviation, its significance, and how it is used across different medical specialties. Whether you are a seasoned healthcare professional, a medical student, or an occupational therapist, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into TDWB and its proper application in patient care.
Introduction to TDWB
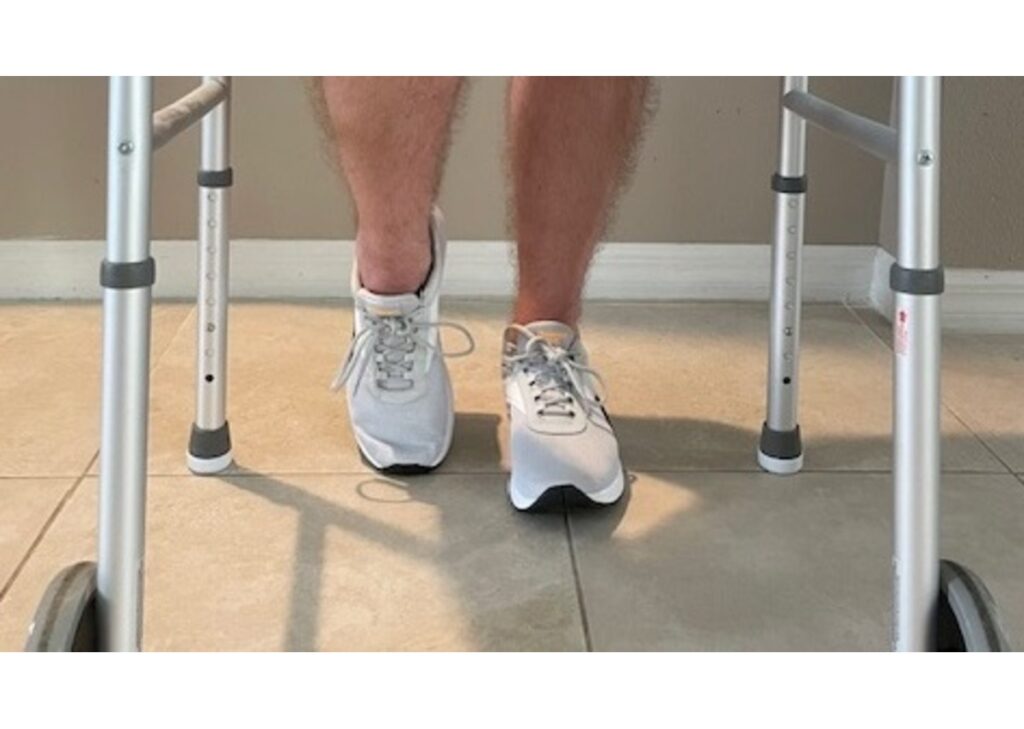
Similar to TTWB (Toe Touch Weight Bearing) TDWB stands for “Touch-Down Weight Bearing.” This term is commonly used in medical facilities, particularly in orthopedics and in therapy to describe a specific type of weight-bearing status for patients recovering from lower limb injuries or surgeries.
Touch-Down Weight Bearing allows a patient to lightly touch their toes to the ground while walking or standing, but without bearing full weight on the affected limb. This technique is crucial in the initial stages of recovery as it aids in maintaining balance and stability while protecting the healing limb.
Importance of TDWB in Healthcare Practices
The TDWB medical abbreviation is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it helps healthcare professionals communicate a patient’s weight-bearing status clearly and concisely. Accurate documentation ensures that everyone involved in the patient’s care understands the limitations and requirements for movement and exercise.
Secondly, TDWB plays a significant role in patient recovery. Adhering to TDWB instructions prevents undue stress on the healing limb, reducing the risk of complications and promoting optimal healing. It allows patients to gradually transition to full weight-bearing as their condition improves.
Lastly, using TDWB correctly can enhance patient outcomes. By following TDWB guidelines, healthcare providers can develop personalized rehabilitation plans that cater to the patient’s specific needs, facilitating a smoother and quicker recovery process.
How TDWB is Utilized in Different Medical Specialties
TDWB is not limited to one area of healthcare. Various medical specialties incorporate this abbreviation into their practice to ensure effective patient care.
Orthopedics
In orthopedics, TDWB is commonly prescribed for patients recovering from fractures, joint replacements, or ligament repairs. Surgeons provide specific weight-bearing instructions, which are crucial for the success of surgical interventions and overall recovery.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists play a pivotal role in guiding patients through the rehabilitation process. They use the TDWB medical abbreviation to design exercise programs that align with the patient’s weight-bearing status. This approach ensures that exercises promote healing without causing harm.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists also rely on TDWB guidelines when helping patients regain independence in daily activities. By understanding and incorporating TDWB into their therapy plans, they can safely teach patients how to perform tasks like dressing, toileting, cooking, and bathing, all while adhering to weight-bearing restrictions.
Common Misunderstandings and Misuse of TDWB
Despite its importance, TDWB is sometimes misunderstood or misused. One common mistake is confusing TDWB with other weight-bearing statuses, such as Non-Weight Bearing (NWB) or Partial Weight Bearing (PWB). Unlike TDWB, NWB means no weight should be placed on the affected limb, while PWB allows for a percentage of the patient’s body weight to be borne.
Another issue is inconsistency in documentation. If healthcare professionals do not clearly specify TDWB in patient records, it can lead to confusion and improper patient care. For example, ambiguity in weight-bearing instructions might result in a patient unknowingly placing too much weight on their healing limb, potentially causing setbacks in recovery.
Additionally, patients themselves may misunderstand TDWB instructions. Without proper guidance, they might either avoid weight-bearing altogether or overestimate the amount of weight they can place on the limb. This underlines the importance of clear communication and education from healthcare providers.
Guidelines on Proper Use of TDWB for Healthcare Professionals
To ensure the correct application of TDWB, healthcare professionals should follow these guidelines:
- Clear Communication: Always clearly communicate TDWB instructions to the patient and their caregivers. Use simple language and provide demonstrations if necessary.
- Consistent Documentation: Accurately document the TDWB medical abbreviation in patient records. Include specific details about the extent of weight-bearing allowed and any timelines for progression.
- Patient Education: Educate patients on the importance of adhering to TDWB guidelines. Explain how it benefits their recovery and provide practical tips for integrating TDWB into their daily activities.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously assess the patient’s progress and adjust weight-bearing instructions as needed. Regular check-ups and monitoring ensure that the patient is on the right track and allows for timely interventions if complications arise.
- Collaborative Approach: Foster collaboration among the healthcare team. Surgeons, physical therapists, and occupational therapists should work together to create a cohesive rehabilitation plan that incorporates TDWB effectively.
Impact of TDWB on Patient Care and Recovery
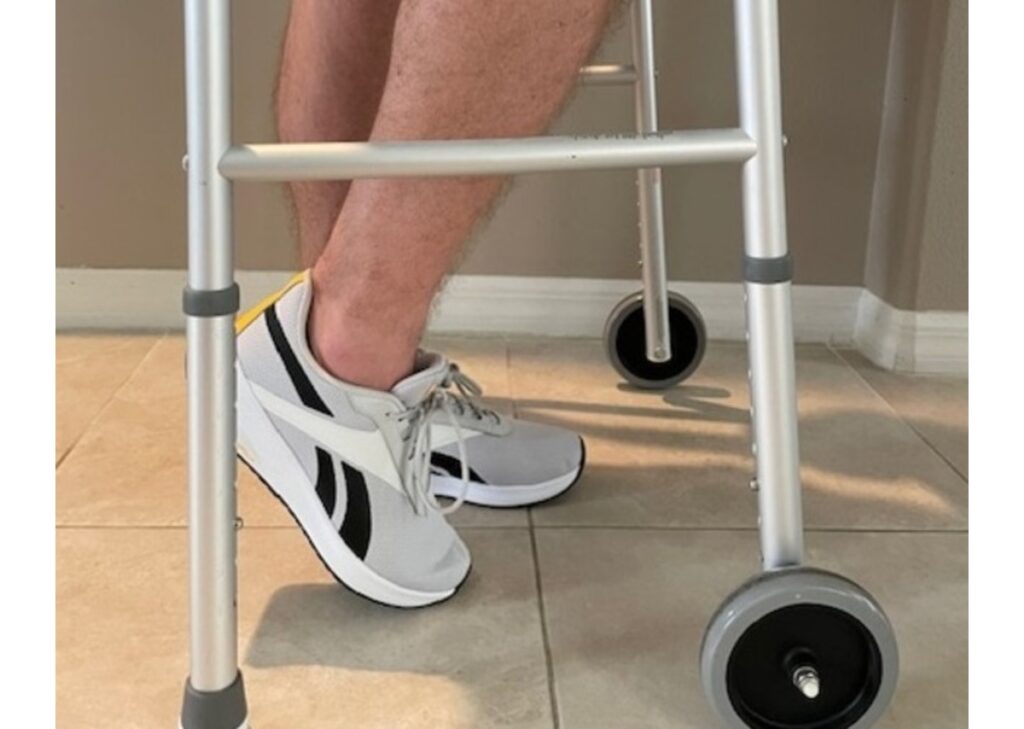
The proper implementation of TDWB has a profound impact on patient care and recovery. Patients who adhere to TDWB instructions experience several benefits, including:
- Reduced Risk of Complications: By limiting weight-bearing during the critical phases of healing, TDWB minimizes the risk of re-injury or complications, such as implant failure or delayed union of fractures.
- Improved Functional Outcomes: Gradual weight-bearing, as recommended by TDWB, helps patients regain strength, balance, and mobility. This progression leads to better functional outcomes and a higher quality of life.
- Enhanced Patient Confidence: Adhering to TDWB guidelines builds patient confidence. Knowing they are following a structured plan designed for their recovery can alleviate anxiety and encourage active participation in rehabilitation.
Conclusion
Understanding the TDWB medical abbreviation is essential for healthcare professionals, medical students, and occupational therapists alike. Its significance in patient care cannot be overstated. By understanding and properly utilizing TDWB, healthcare providers can enhance communication, improve patient outcomes, and contribute to more efficient and effective recovery processes.
Continuous learning and adherence to best practices in medical abbreviations like TDWB are crucial for delivering high-quality care. For those seeking further guidance or personalized training, consider reaching out to specialized courses or workshops that offer in-depth knowledge and hands-on experience in medical terminology and patient management. Incorporating TDWB into your daily practice is not just about following a guideline; it’s about committing to the well-being and optimal recovery of your patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does TDWB stand for?
TDWB stands for “Touchdown Weight Bearing.” It indicates that a patient is allowed to place their foot on the ground for balance and support but should not bear full weight on the affected limb.
How long should a patient adhere to TDWB instructions?
The duration for adhering to TDWB varies by individual and surgical procedure. It is essential to follow the specific guidance provided by healthcare professionals, as they will set timelines based on the patient’s recovery progress.
Can TDWB be adjusted during recovery?
Yes, TDWB instructions can be adjusted based on the patient’s progress in healing. Regular assessments by healthcare providers will help determine when it is appropriate to transition to Partial Weight Bearing (PWB) or Full Weight Bearing (FWB).
How can patients ensure they are following TDWB correctly?
Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare team, seek clarification on any unclear instructions, and participate in educational sessions about their weight-bearing status. Additionally, rehabilitative exercises should be performed under the supervision of physical or occupational therapists.
What are the consequences of not following TDWB guidelines?
Failing to adhere to TDWB guidelines can lead to complications such as delayed healing, increased pain, or re-injury of the affected limb. This emphasizes the importance of understanding and adhering strictly to the recommended weight-bearing limitations.
References
- McCarthy, C., & Morgan, R. (2021). Understanding Weight Bearing Restrictions: A Clinical Perspective. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 53(5), 457-465. doi:10.2340/16501977-2911.
- Johnson, P. D., & Smith, K. R. (2020). The Importance of Communication in Patient Recovery: A Focus on Weight Bearing Practices. The British Journal of Surgery, 107(3), 342-349. doi:10.1002/bjs.11533.
- Turner, A. R., & Jackson, M. (2019). Patient Compliance with Rehabilitation Protocols: Implications for Recovery. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 100(12), 2315-2322. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2019.06.013.
- Brown, T. J., & Green, L. S. (2022). Rehabilitation Strategies Following Surgical Procedures: An Overview of Weight Bearing Guidelines. Journal of Orthopedic Research, 40(1), 112-119. doi:10.1002/jor.24689.
- Health Resources and Services Administration. (2023). Best Practices for Patient Education in Weight-Bearing Activities. Retrieved from https://www.hrsa.gov/weightbearingguidelines.
Recently Featured OT Insider Posts
WNL Medical Abbreviation: How it’s used in Healthcare
Therapeutic Use of Self for Transformative Occupational Therapy
OT Frames of Reference: Practical Applications for Patient Care
Inpatient Occupational Therapy: How it Works to Revitalize Lives
KELS Assessment: How to Use it to Unlock Independence
