Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is a critical tool in the healthcare professional’s toolkit, especially for occupational therapists. This hands-on technique helps in assessing the strength of individual muscles or muscle groups based on their ability to resist pressure. But what exactly is MMT, and why is it so significant in healthcare practice?
Introduction to Manual Muscle Testing (MMT)
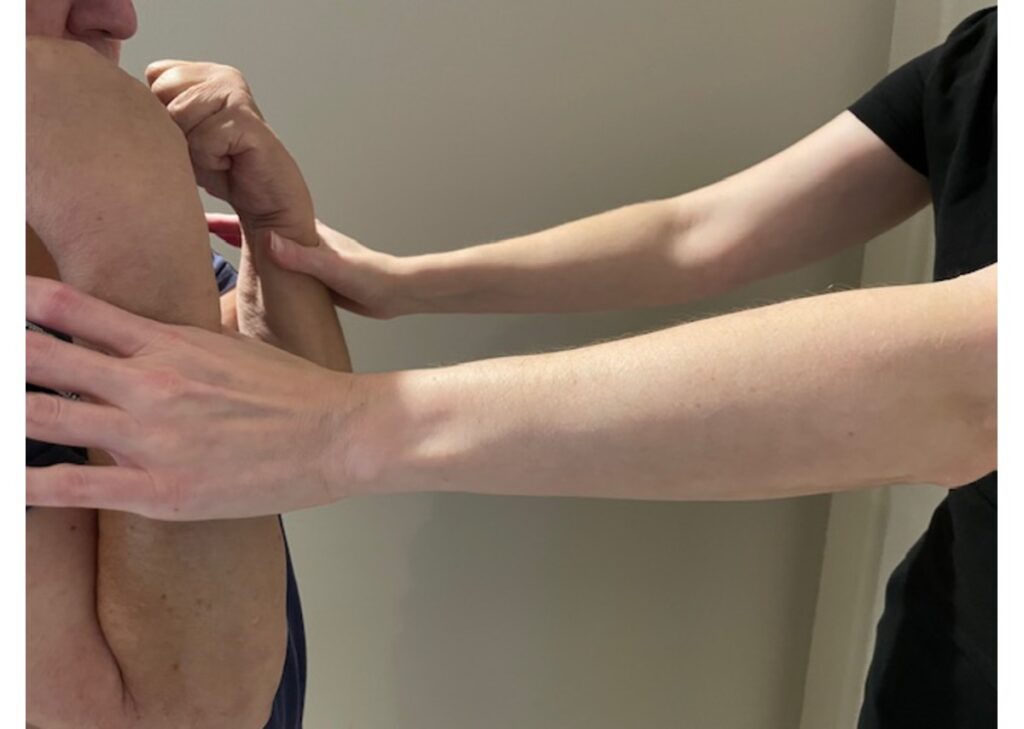
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is a standardized method used by healthcare professionals to evaluate muscle strength. It relies on the practitioner’s ability to apply resistance and measure the muscle’s performance against this resistance. MMT is crucial for diagnosing and tracking the progress of patients with neuromuscular disorders, musculoskeletal injuries, and other conditions affecting muscle function.
The Significance of MMT in Healthcare Practice
Manual Muscle Testing plays a pivotal role in healthcare for several reasons. Firstly, it aids in the diagnosis of various conditions, helping to localize muscle impairments. Secondly, MMT guides treatment plans, as the results inform the type of interventions needed. Lastly, it provides a baseline for tracking patient progress over time, making it easier to adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Understanding MMT Grades and the MMT Scale
MMT grades range from 0 to 5, offering a clear and concise way to document muscle strength. The manual muscle testing scale helps standardize these grades, ensuring consistent evaluation across different practitioners.
The Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) Scale Explained
The MMT scale is as follows:
- Grade 0: No visible or palpable muscle contraction.
- Grade 1: Flicker of contraction but no movement.
- Grade 2: Full range of motion without gravity.
- Grade 3: Full range of motion against gravity but no resistance.
- Grade 4: Full range of motion against moderate resistance.
- Grade 5: Full range of motion against maximum resistance.
Why Manual Muscle Testing Grades Matter
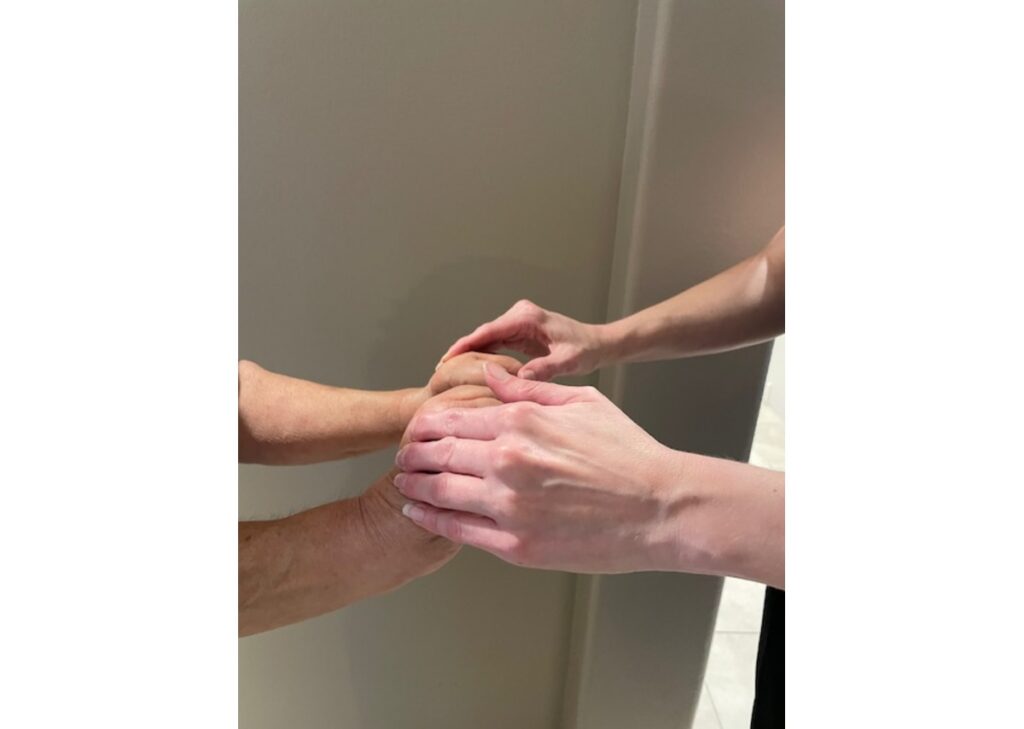

Understanding MMT grades is essential for accurate patient assessment. These grades help quantify muscle strength, enabling targeted treatment interventions. Consistency in using the MMT scale ensures reliable communication among healthcare providers, enhancing patient care.
The Procedure of Conducting MMT
Conducting Manual Muscle Testing involves several steps to ensure accurate results. Firstly, the patient should be positioned appropriately to isolate the muscle or muscle group being tested. Secondly, the practitioner applies resistance in a controlled manner. Finally, the muscle’s ability to resist this force is graded according to the MMT scale.
Step-by-Step Guide to MMT
- Positioning: Ensure the patient is in a position that isolates the muscle group.
- Stabilization: Stabilize the proximal segment to avoid compensatory movements.
- Application of Resistance: Apply resistance gradually, ensuring it is perpendicular to the muscle’s action.
- Assessment: Evaluate the muscle’s performance and assign an MMT grade.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Inconsistent resistance application and improper positioning can lead to inaccurate MMT results. Always ensure the resistance is applied smoothly and the muscle is adequately isolated.
Common Uses of MMT in Occupational Therapy
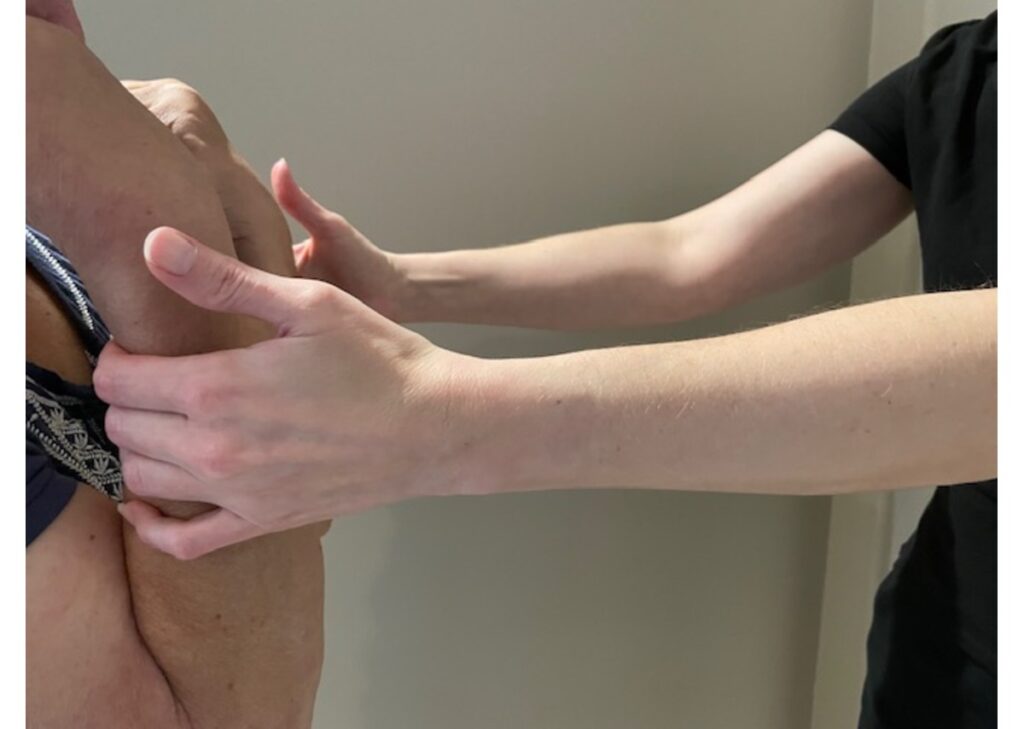
In occupational therapy, MMT is indispensable for developing and monitoring rehabilitation programs. It helps therapists understand the extent of muscle weakness, which is crucial for customizing patient interventions.
Rehabilitation Planning
MMT informs the creation of personalized rehabilitation plans. By identifying specific muscle weaknesses, therapists can design targeted exercises to improve muscle function.
Patient Progress Tracking
Regular MMT assessments allow therapists to track improvements in muscle strength. This ongoing evaluation helps in adjusting treatment plans to meet evolving patient needs.
Enhancing Patient Outcomes
By providing precise data on muscle strength, MMT enables more effective interventions. This precision leads to better patient outcomes, as treatments are tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Challenges and Limitations of MMT
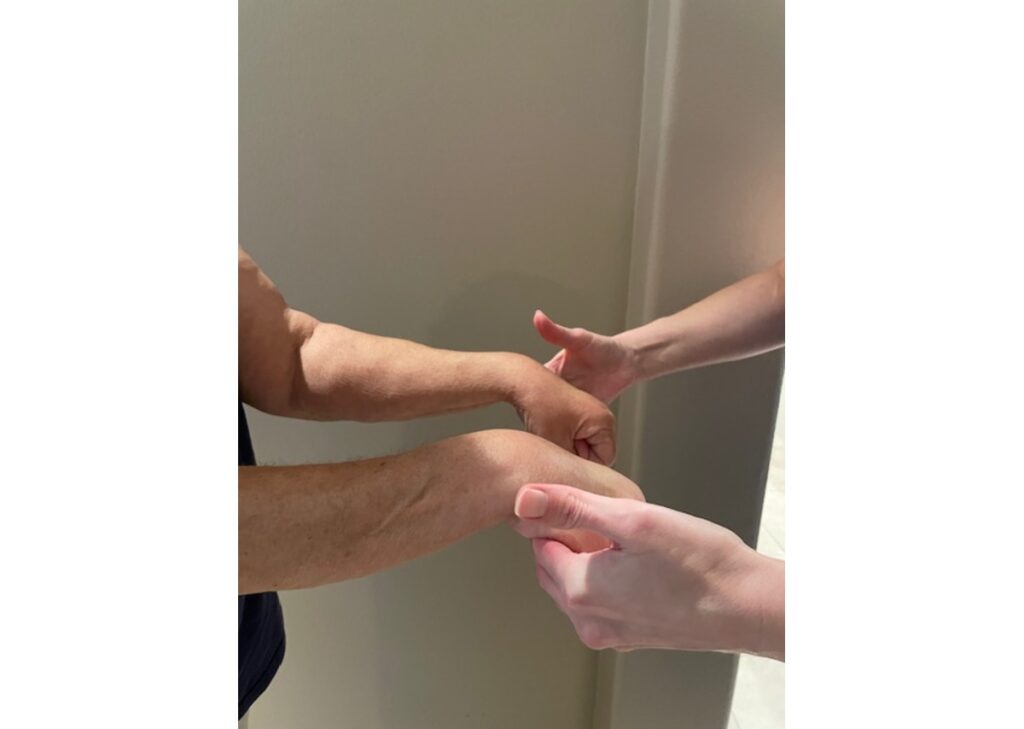

Despite its benefits, MMT has certain limitations. The subjective nature of resistance application can lead to variability in results. Additionally, MMT may not be accurate or appropriate when testing patients with severe pain or neurological impairments.
Subjectivity in Resistance Application
The primary challenge in MMT lies in the subjective nature of resistance application. Different practitioners may apply varying levels of force, leading to inconsistent results.
Patient-Related Limitations
Patients experiencing severe pain or neurological issues may struggle to participate in MMT fully. In such cases, alternative assessment methods should be considered.
Addressing Limitations
Training and standardization can help mitigate some of these challenges. Ensuring practitioners follow consistent procedures and use objective measures wherever possible will improve MMT accuracy.
How Technology is Innovating MMT
Technological innovations are improving the precision and dependability of Manual Muscle Testing. The use of digital dynamometers and similar instruments delivers objective measurements, thereby minimizing the subjectivity that often accompanies conventional MMT methods.
Digital Dynamometers
Digital dynamometers offer precise measurements of muscle strength, providing objective data that complements traditional MMT. These devices eliminate the variability in resistance application, ensuring consistent results.
Software Solutions
Software applications can assist in recording and analyzing MMT data, making it easier to track patient progress over time. These tools often integrate with electronic health records, streamlining the documentation process.
Future Innovations
Future advancements may include AI-driven tools that offer real-time feedback during MMT assessments. These innovations will further enhance the precision and utility of Manual Muscle Testing in healthcare.
Practical Tips for Accurate MMT Results
Achieving accurate MMT results requires attention to detail and consistent practices. Here are some practical tips for healthcare professionals.
Standardize Your Technique
Ensure consistency in your MMT technique by adhering to standardized procedures. This consistency will improve the reliability of your assessments.
Use Objective Tools
Whenever possible, incorporate objective tools like digital dynamometers into your MMT practice. These tools provide precise measurements, reducing subjectivity.
Continuous Training
Invest in continuous training to stay updated on best practices and technological advancements in MMT. Regular training will enhance your skills and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Manual Muscle Testing is a vital tool for healthcare professionals, offering valuable insights into muscle strength and function. Understanding MMT grades and the MMT scale is crucial for accurate assessments and effective treatment planning. While challenges exist, technological innovations are continually improving the precision and reliability of MMT. By following standardized procedures and incorporating objective tools, healthcare professionals can achieve accurate and consistent MMT results, ultimately enhancing patient care.
For those interested in exploring more about MMT or seeking to refine their skills, numerous resources and references are available. Consider integrating these practices into your routine to better serve your patients and advance your professional expertise.
The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as, nor should it be considered, professional or medical advice. Always consult a professional regarding your specific medical issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Manual Muscle Testing (MMT)?
Manual Muscle Testing is a clinical assessment method used to evaluate muscle strength and function. It involves the application of resistance against a muscle’s contraction to determine its performance and assign a corresponding grade.
Why is MMT important in rehabilitation?
MMT is crucial in rehabilitation as it helps therapists identify muscle weaknesses, tailor rehabilitation plans, and track patient progress. Accurate assessments enable customized interventions that enhance patient recovery.
How is MMT graded?
MMT grades range from 0 to 5, with 0 indicating no muscle contraction and 5 indicating normal strength. Each grade reflects the muscle’s ability to contract against varying levels of resistance.
What are the limitations of MMT?
Limitations of MMT include the subjectivity in resistance application, which can lead to variability in results, and the unsuitability for patients with severe pain or neurological impairments.
How can technology improve MMT outcomes?
Technology, like digital dynamometers, provides objective measurements of muscle strength that reduce subjectivity in assessments. Software solutions can assist in data tracking and analysis, enhancing overall accuracy and reliability.
Are there alternative assessment methods to MMT?
Yes, for patients unable to participate in MMT due to pain or neurological issues, alternative assessment methods such as functional tests and observational assessments may be considered to evaluate muscle function.
References
- Mierau, A., & Kahn, S. (2020). Manual Muscle Testing: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 32(3), 295-303. doi:10.1589/jpts.32.295
- Gajdosik, R. L., & Albert, T. R. (2018). Reliability of Manual Muscle Testing in Physical Therapy: A Systematic Review. Physical Therapy Reviews, 23(4), 211-228. doi:10.1080/10833196.2018.1462137
- Ward, J., & Leach, L. (2019). Digital Tools for Measurement of Muscle Strength: Advancements in Technology. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research, 42(2), 95-101. doi:10.1097/MRR.0000000000000402
- Crouch, A. L., & MacMillan, K. (2017). Standardization of Muscle Testing Techniques: Implications for Clinical Practice. Physical Therapy Journal, 67(8), 972-979. doi:10.1093/ptj/pzx045
- American Physical Therapy Association. (2021). Clinical Guidelines for Manual Muscle Testing. Retrieved from www.apta.org
- Black, R., & Smith, A. (2022). Assessing Muscle Function in Patients: An Evidence-Based Approach. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, 59(1), 35-48. doi:10.1682/JRRD.2022.01.0010
Recently Featured OT Insider Posts
Understanding BUE (Bilateral Upper Extremity) in Medical Practice
Fine Motor Skills for Adults in Occupational Therapy
Gait Belt Techniques for Occupational Therapy
SBA (Stand-by Assist) in Occupational Therapy for Patient Care
Understanding the HOB Medical Abbreviation in Patient Care
Navigating Multiple Sclerosis (MS) with Occupational Therapy
